


|
Background Color |

|
|
|
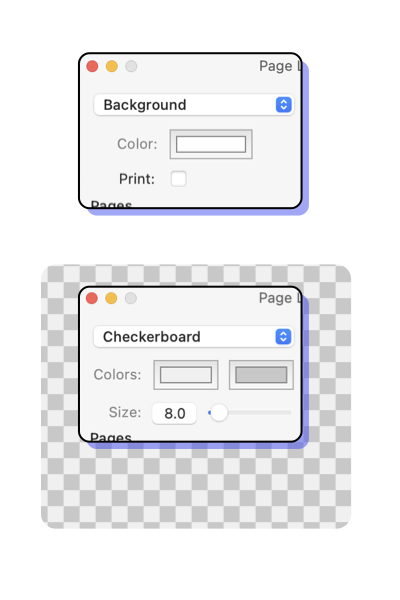
A drawing may have a non-white background color and this color may be printed or used only for the display screen. The background color is like a canvas of a painting. This color is applied to the entire drawing before any graphics are drawn. The background is always the first graphic element in the Drawing Order . For some drawing projects it is desirable to clearly visualize transparency. A common method is to show graphics against a checkerboard background. The top left popup menu provides a choice for this technique. The background color is drawing specific, each drawing may have a different color background. Color changes apply to the top drawing window, not to all drawings. The background color is saved in the file with the rest of the data for the drawing. Use the Defaults panel to change the background color for all new drawings. Background Color’s colorwell is found on the Page Layout panel. This is accessed from the File main menu, near the bottom of the menu. The top left popup menu provides access to both the solid background settings and those for a transparency checkerboard. The popup menu has dual function: selecing the one of the two parameter sets, and defining the background display technique (solid, or checkerboard).
Be especially careful when using black as a background color. If you elect to print the background, all pages will be filled with black as a first drawing step. This can use up an ink cartridge quickly and is probably not the desired action. If you really want a black printed background, buy black paper. If you plan to print the drawing on colored paper then set the background color to the color of the paper and the computer display will properly represent the visual color relationships of the drawing. In this case you still do not check the print background color check-box. The Transparency Checkerboard is never exported or printed. It is only used as a background for the on-screen display. The checkerboard represents or visually indicates "Nothing" or fully transparent areas of the drawing. Notice a checkerboard pattern uses two colors to visually indicate clear or transparent regions of the drawing. The "two" colors are needed to distinguish an area of the drawing that might match a single background indicating color. For example, white is a convenient background-indicating color, it matches the "white" of un-colored paper and provides brightness to the screen for crisper vision through constricted pupils. But a graphic such as a rectangle might have a white fill which is then indistinguishable from a transparent non-filled rectangle. The two colors of the checkerboard will (if the rectangle is "large") indicate the drawing construction. |